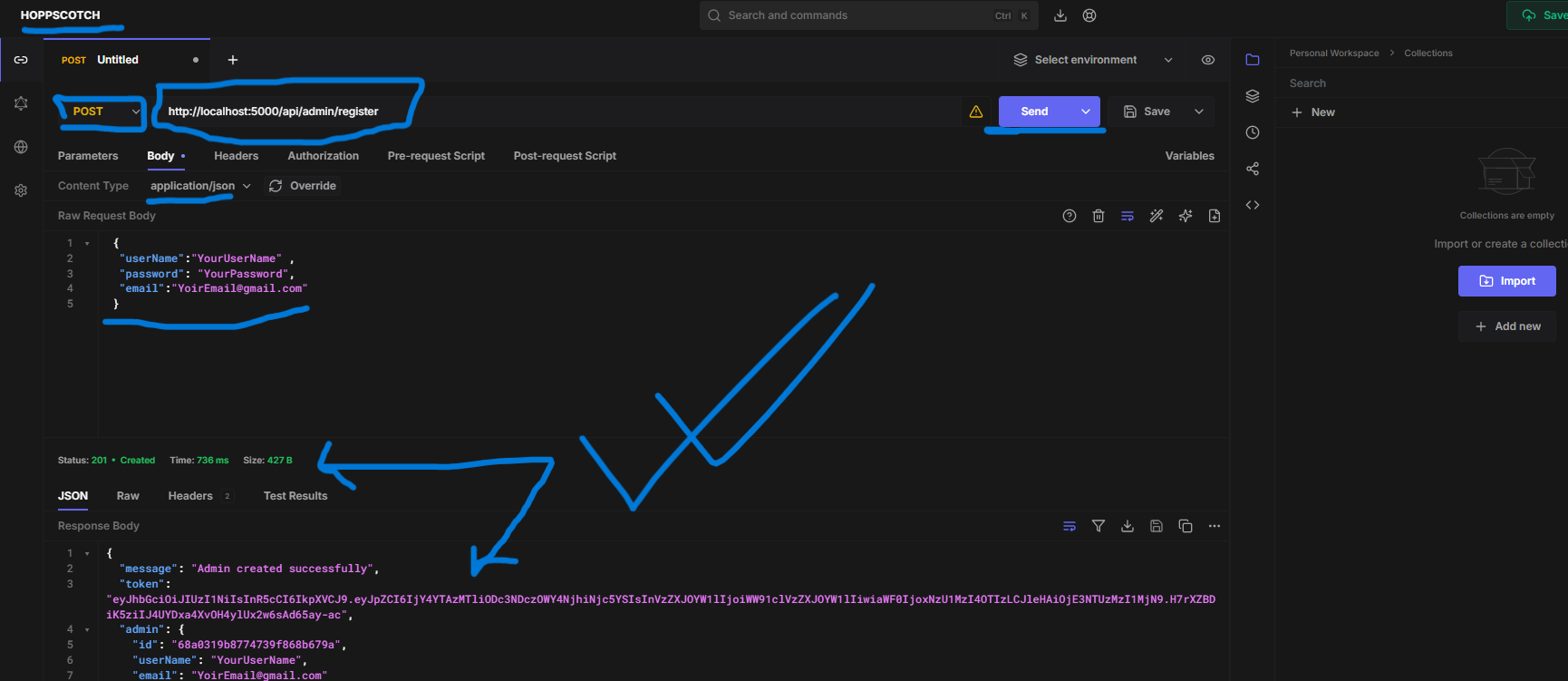
Setting Up Environment Variables
1Create a .env File
In your project's root directory, create a new file named
.env
.env file should never be
committed to version control. Make sure to add it to your
.gitignore file.
2Configure Environment Variables
Add the following configuration to your .env file:
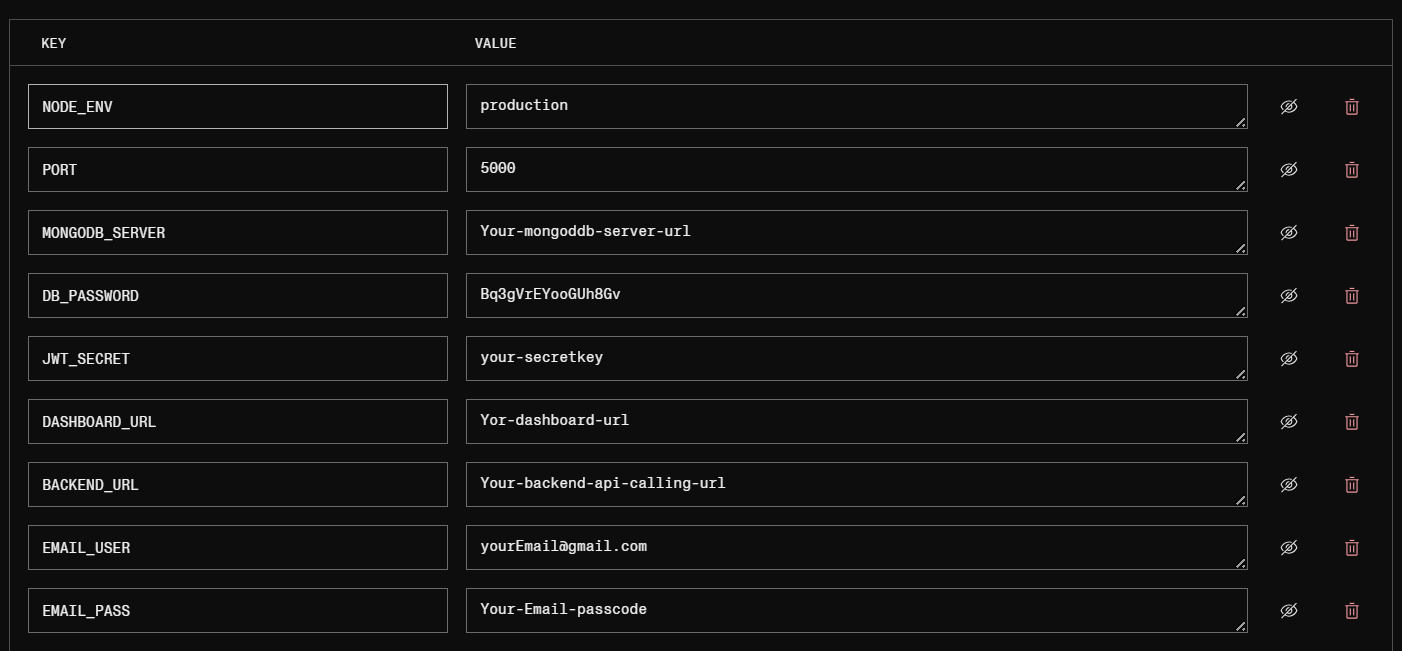
NODE_ENV=development PORT=5000 MONGODB_URI=mongodb+srv://your_username:your_password@cluster0.xxxxx.mongodb.net/your_database?retryWrites=true&w=majority DB_PASSWORD=your_mongodb_password JWT_SECRET=secretkey
-
MONGODB_URI: Replace with your actual MongoDB
Atlas connection string
You can find your connection string in MongoDB Atlas:
- Go to your Cluster dashboard
- Click "Connect" button
- Select "Connect your application"
- Copy the connection string
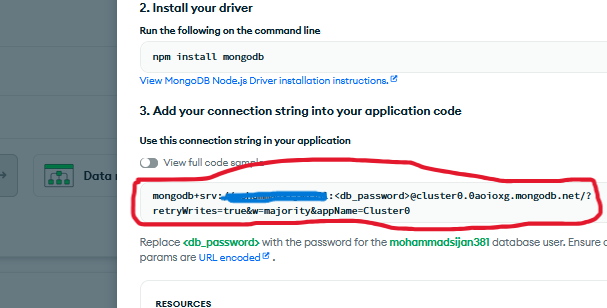
Example: Where to find your MongoDB connection string in Atlas
-
DB_PASSWORD: Use your actual MongoDB user
password (not your Atlas account password)
This is the password you created when setting up database access:
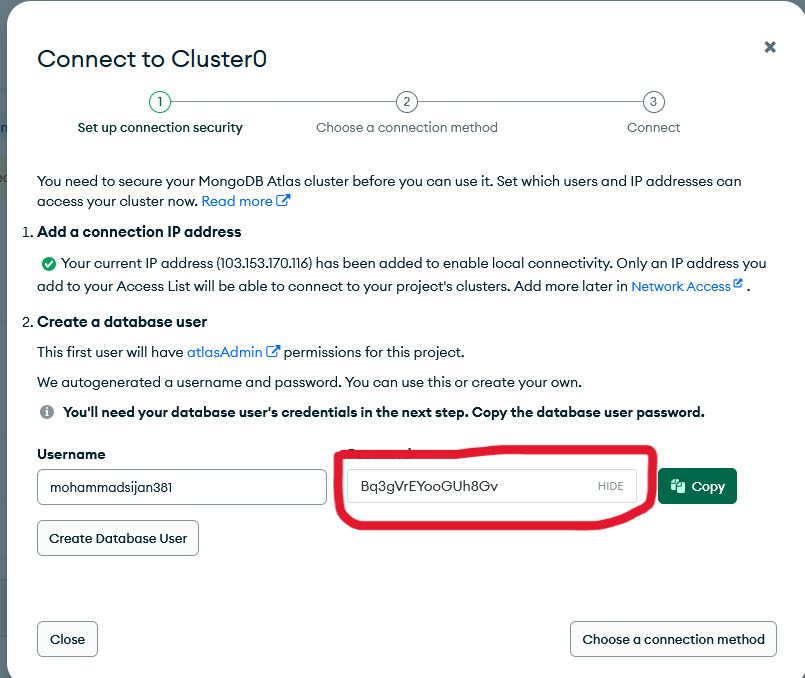
Example: Database user password setup in MongoDB Atlas
- Keep this file secure and never share it publicly
- These values are examples - use your actual credentials
NODE_ENV=development PORT=5000 MONGODB_URI=mongodb+srv://devuser:SecurePass123@cluster0.0aoioxg.mongodb.net/myappdb?retryWrites=true&w=majority DB_PASSWORD=SecurePass123
Note how the password appears in both MONGODB_URI and DB_PASSWORD in this example.
3Create a MongoDB Cluster (If You Don't Have One)
If you don't already have a MongoDB Atlas cluster set up, follow our comprehensive guide:
View MongoDB Atlas Setup Guide- Create a free M0 cluster (perfect for development)
- Set up a database user (different from your Atlas account)
- Whitelist your IP address (or allow access from anywhere for development)


4Set Up Your Development Environment
Open Project in VS Code
- Launch Visual Studio Code
- Click "File" → "Open Folder"
- Select your backend project folder
Install Node.js (If Not Already Installed)
-
Check if Node.js is installed by running in terminal:
node -v
- If not installed, download and install from: https://nodejs.org/ (LTS version recommended)
Install Dependencies
- Open the terminal in VS Code (Ctrl+` or Terminal → New Terminal)
-
Run the following command to install all required packages:
npm install
- Wait for all dependencies to be installed
- Make sure you have a stable internet connection
- Try running as administrator if you're on Windows
- Check the error message for specific package issues